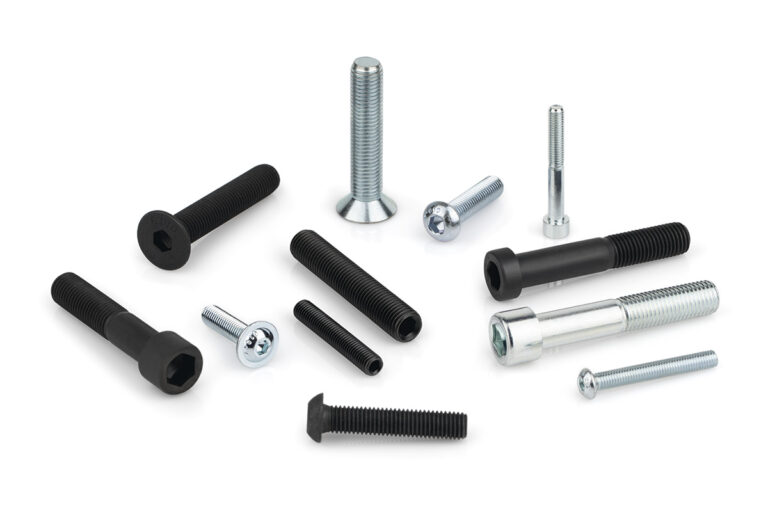
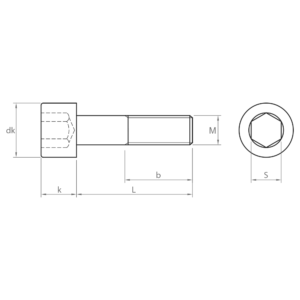
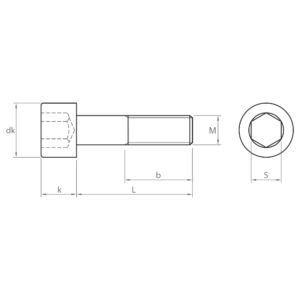
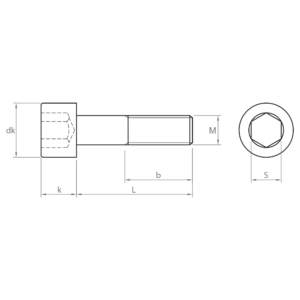
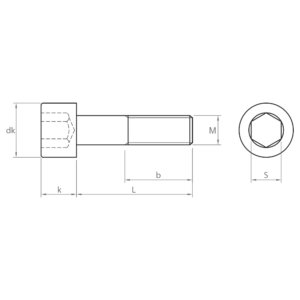
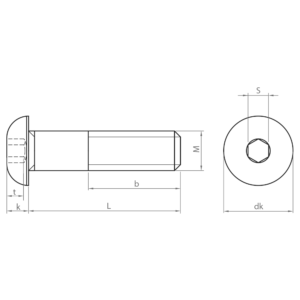
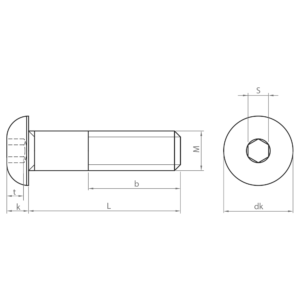
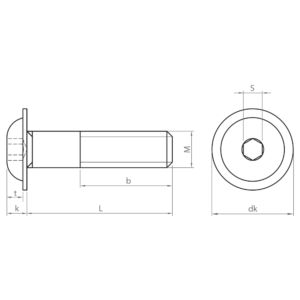
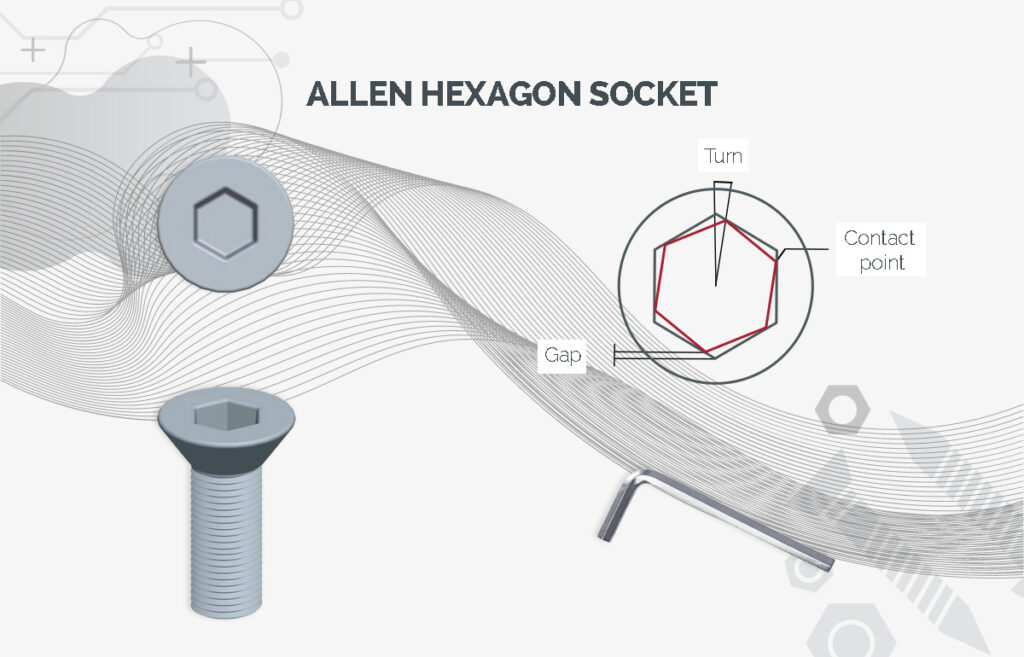
Socket screws, also known as hexagon socket head cap screws, are indispensable fasteners in a wide variety of industrial sectors. Their design, with a hexagon socket in the head, allows for high torque and facilitates their use in confined spaces.
Origin of socket screws
The history of the socket screw dates back to the early 20th century. Although the concept of a hexagonal recess in a screw had existed before that time, it was in the middle of the 20th century that its use became popular and standardised. The name ‘Allen’ comes from the Allen Manufacturing Company, which was one of the first to mass-produce these socket screws and the special spanners to fit them.
However, the invention of the socket screw is not attributed to a single person, but is the result of an evolutionary process in which different manufacturers and engineers contributed to its development and refinement. The hexagonal head geometry offers several advantages over other types of screw heads, such as increased wear resistance and the possibility of applying higher tightening torques.
The high torque and ease of the Allen key, coupled with the growing demand for more efficient and versatile fastening systems, contributed to the rapid adoption of socket screws in a variety of industries.
Types of socket screws
Socket screws are classified according to different international standards, such as DIN and ISO.
These are the socket screws available according to DIN standards:
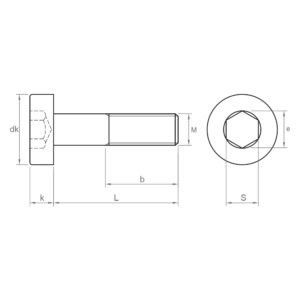
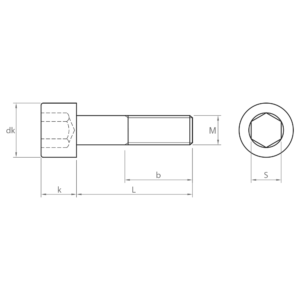
- DIN 912: the standard socket screw with cylindrical head and hexagon socket and partial thread. It is commonly used in industry due to its versatility and firm grip. It is available in carbon steel and A2 and A4 stainless steel; zinc-plated and black coatings; and grades 8.8, 10.9 and 12.9. This socket screw is similar to ISO 4762.
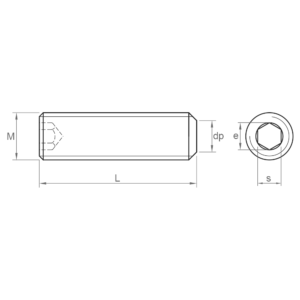
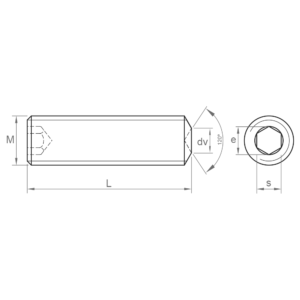
- DIN 913: Known as an Allen stud or grub screw, it is similar to DIN 912, but without the head. It has a flat tip and is used to immobilise elements. It is available in carbon steel and A2 stainless steel; black coating and 45H quality. It is similar to ISO 4026.
- DIN 916: Allen stud or headless screw. It has a sharp point and is used to retain elements and for a certain aesthetic purpose as it is flushed with the surface. It is available in carbon steel and A2 stainless steel; black coating and 45H quality. It is similar to ISO 4029.
- DIN 7984: socket screw with low head and partial thread, especially suitable for applications where space is limited or where a more aesthetic appearance is required as it has a lower profile than DIN 912. Available in carbon steel with black coating and quality 8.8.
- DIN 7991: socket screw with countersunk or flat head and partial thread. These screws allow the head to sink into the material, resulting in a smooth, even surface. Available in carbon steel and stainless steel A2 and A4; zinc-plated and black coatings; and quality 10.9.
Socket screws available according to ISO standards:
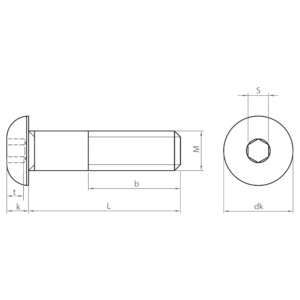
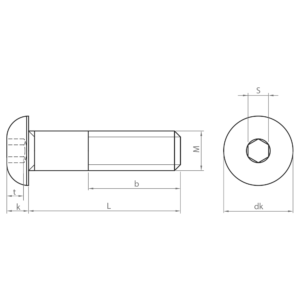
- ISO 7380-1: socket screw with round head and partial thread. Available in carbon steel and stainless steel A2 and A4, zinc-plated and black coatings and quality 10.9.
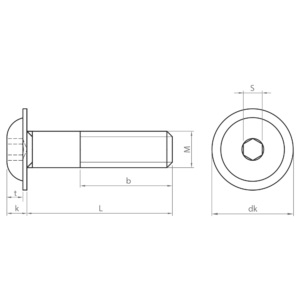
- ISO 7380-2: similar to ISO 7380-1, but with an integrated washer under the head. The integrated washer distributes the load evenly, preventing damage to the material and improving clamping. Available in carbon steel; zinc plated and black coatings; and quality 10.9.
Advantages and disadvantages of socket screws
The hexagonal geometry inside the socket screw head offers several advantages over other types of screw heads. Unlike cross or flat slots, the hexagonal recess allows a higher torque to be applied without damaging the screw head. In addition, the Allen key fits more securely into the socket, reducing the risk of slippage and allowing a more precise tightening. In summary, the main advantages are:
- High tightening torque: Thanks to the geometry of the hexagon head, high tightening torques can be achieved without damaging the screw.
- Easy installation: Allen keys allow efficient and precise force transmission. The use of this tool is more comfortable and safer, reducing the risk of injury and fatigue.
- Increased vibration resistance: thanks to the hexagonal shape of the hexagon socket screw, which distributes the force evenly.
- Corrosion resistance: coatings such as zinc plating and black offer protection against rust.
- Wide variety of materials and grades: stainless steel, carbon steel, and different degrees of mechanical strength to suit any application. In addition, they are available in a wide range of sizes and dimensions to meet the requirements of each project.
- Difficulty of automation: insertion of the Allen key into the hexagon socket can be complicated in automated processes.
- Risk of ‘crowning’: over-tightening or an unsuitable tool can damage the head of the screw.
Main characteristics of the socket screws
How to choose the right socket screw
The choice of the right socket screw depends on a number of factors:
- Material: consider the material of the parts to be joined and the environmental conditions.
- Load: select a screw with adequate mechanical strength to withstand the applied load.
- Available space: choose the head and length of the screw according to the available space.
- Aesthetics: in some applications, the visual appearance of the fastener may be important.
Most common applications of socket screws
Socket screws are used in a wide range of sectors:
- Automotive: fastening of mechanical components, engine assembly, body panels, seats, etc.
- Construction: assembly of metal structures, fixing of machinery, urban furniture.
- Machinery: fixing of components in industrial machinery, agricultural equipment, etc.
- Furniture and carpentry: assembly of furniture, shelving, joining of wooden parts, etc.
- Electronics: fixing electronic components on boards and housings.
- Sports: manufacture of bicycles, sports equipment, etc.
- General maintenance and repair: fastenings in machinery, vehicles and electrical equipment, among others.

In addition to DIN and ISO standards, we also offer socket screws with special features through our special coating services and fasteners to drawing.
Socket screws are versatile and secure fasteners, widely used in various industries. At CHAVESBAO we offer you a wide range of socket screws in different materials, coatings and qualities, to adapt to your specific needs. If you need advice to choose the right screw for your project, do not hesitate to contact us.